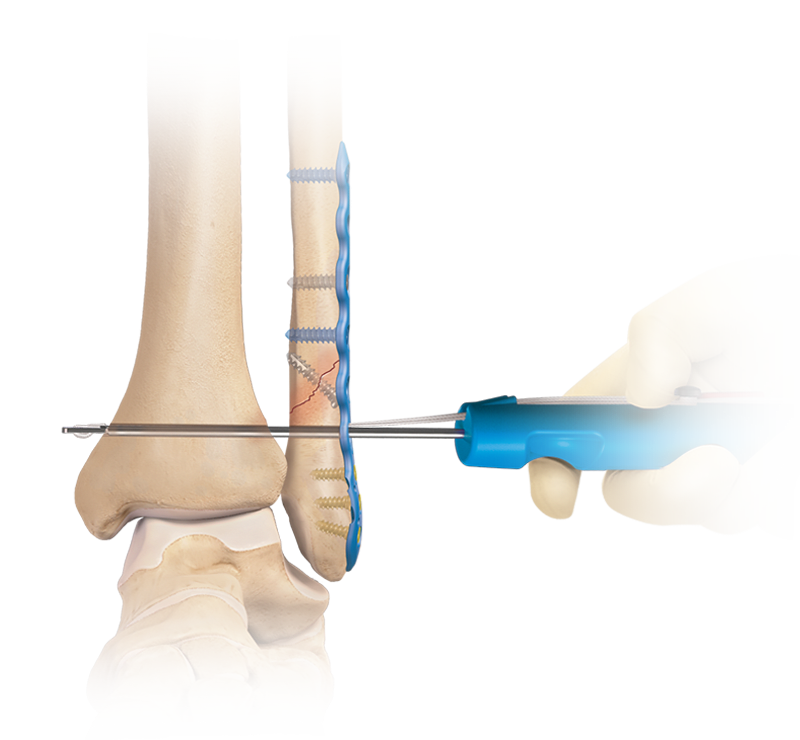
Syndesmosis Injury
The Syndesmosis TightRope® XP implant system features a unique delivery mechanism that allows surgeons to insert the implant without pulling a needle through the medial skin. Tensioning handles and a new trocar-tipped drill bit have been added to the implant system.
Advantages of the Syndesmosis TightRope XP implant system include:
- Improved reduction when compared to syndesmosis screws1
- Improved maintenance of reduction when compared to syndesmosis screws2
- No need for routine implant removal
- Supports early weightbearing and accelerated rehabilitation1
- Allows for physiologic motion of the syndesmosis following reduction and fixation
- Improved patient outcomes compared to syndesmosis screws3-5
References
1. Naqvi GA, et al. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(12):2828-2835. doi:10.1177/0363546512461480.
2. Cottom JM, et al. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009;48(6):620-630. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2009.07.013.
3. Laflamme M, et al. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(5):216-223. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000245.
4. Shimozono Y, et al. Am J Sports Med. 2018 Nov 26:0363546518804804 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1177/0363546518804804.
5. Andersen MR, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(1):2-12. doi:10.2106/JBJS.16.01011.
The Syndesmosis TightRope® XP implant system features a unique delivery mechanism that allows surgeons to insert the implant without pulling a needle through the medial skin. Tensioning handles and a new trocar-tipped drill bit have been added to the implant system.
Advantages of the Syndesmosis TightRope XP implant system include:
- Improved reduction when compared to syndesmosis screws1
- Improved maintenance of reduction when compared to syndesmosis screws2
- No need for routine implant removal
- Supports early weightbearing and accelerated rehabilitation1
- Allows for physiologic motion of the syndesmosis following reduction and fixation
- Improved patient outcomes compared to syndesmosis screws3-5
References
1. Naqvi GA, et al. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(12):2828-2835. doi:10.1177/0363546512461480.
2. Cottom JM, et al. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009;48(6):620-630. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2009.07.013.
3. Laflamme M, et al. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(5):216-223. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000245.
4. Shimozono Y, et al. Am J Sports Med. 2018 Nov 26:0363546518804804 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1177/0363546518804804.
5. Andersen MR, et al. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(1):2-12. doi:10.2106/JBJS.16.01011.